How to Use Tranexamic Acid for Dark Spots, Melasma, and Acne Marks (Backed by Science)
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases—at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I truly believe in.
Let’s talk dark spots — because honestly, why are they so clingy? You treat your skin right, you wear the sunscreen, and still… BAM. Another stubborn patch pops up like an uninvited guest who brought luggage.
For years, hydroquinone was the ride-or-die for fading hyperpigmentation. And sure, it works — but it’s a bit like using a sledgehammer to hang a picture frame. You might get the job done, but don’t be surprised if there’s a mess to clean up. Think irritation, rebound pigmentation, and long-term safety concerns.
Enter tranexamic acid for dark spots — the under-the-radar overachiever that derms have been quietly obsessing over. Originally used in medicine to stop bleeding (yes, really), it turns out this ingredient also blocks one of the key steps in melanin production. And unlike its flashier cousin hydroquinone, tranexamic acid for melasma works more gently, making it ideal for sensitive skin types.
So what’s the deal — is this a one-hit wonder or your new dark-spot BFF? And in the battle of tranexamic acid vs hydroquinone, which actually wins? Let’s science our way through it.
What Is Tranexamic Acid & How Does It Work
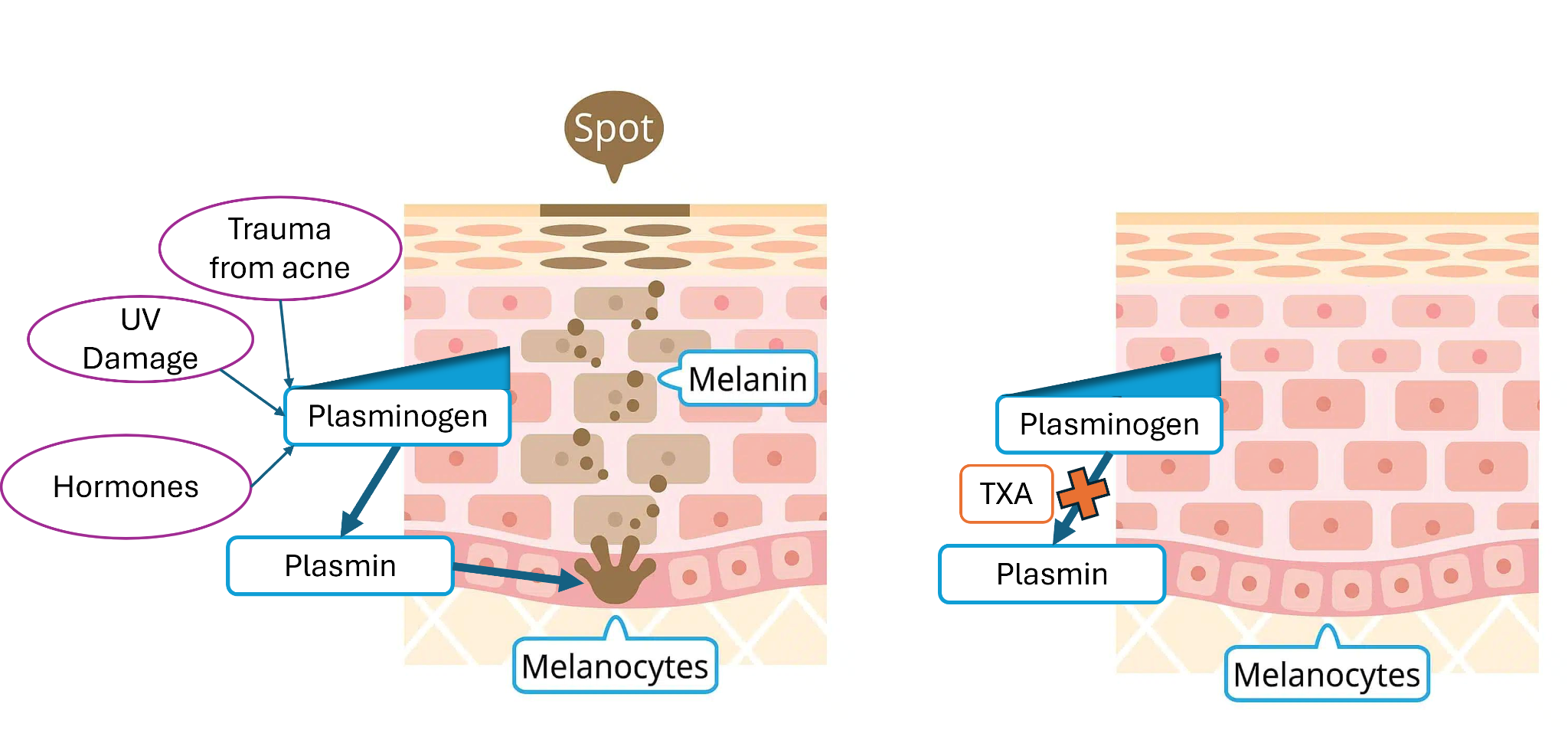
UV, hormones, and inflammation can all lead to activated plasminogen, which turns into plasmin. Plasmin then signals melanocytes to make extra melanin — leading to dark spots. Tranexamic acid (TXA) blocks this step, keeping pigment production under control.
Let’s Break It Down:
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is one of those ingredients that sounds intimidating, but really it’s just a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. It was originally used to help stop excessive bleeding — like during surgery or for heavy periods. But skincare researchers had one of those “wait a minute…” moments when they noticed that patients on oral TXA were seeing unexpected brightening in their skin tone.
So what’s going on in there?
TXA works by inhibiting the plasminogen → plasmin conversion in skin cells. Plasmin is part of the inflammatory cascade that leads to — you guessed it — melanin overproduction. By blocking this, TXA helps reduce hyperpigmentation before it even starts cooking.
It also prevents UV-triggered melanocyte activation and decreases the interaction between melanocytes (pigment cells) and keratinocytes (skin cells that get the melanin handed off). TL;DR: TXA stops pigment before it becomes a problem.
Topical vs Oral vs Other Routes
You’ll see TXA show up in a few forms, but for over-the-counter skincare, we’re talking topical tranexamic acid serums. They’re safe, effective, and don’t require a derm visit.
Topical: Ideal for daily use. Concentrations usually range from 2–5% in most serums.
Oral: Reserved for derm-prescribed cases, especially resistant melasma. Effective, but not DIY territory.
Microneedling + TXA: Trending, but definitely a pro-level treatment.
What the Research Says — Effectiveness & Studies
Tranexamic Acid vs. Hydroquinone: Who Wins?
Let’s address the serum-soaked elephant in the room: is tranexamic acid actually better than hydroquinone for dark spots?
📚 Several head-to-head studies say: kinda, yeah.
Hydroquinone still fades pigmentation faster, but it comes with a whole suitcase of potential issues — irritation, rebound melasma, ochronosis (a rare but scary side effect), and long-term skin sensitivity.
TXA? It’s slower, but it’s also gentler, safer, and suitable for longer use. In one 2021 randomized trial, TXA 5% gel was almost as effective as 4% hydroquinone for melasma, but with significantly less irritation and better patient satisfaction by week 12 (Sarkar et al., 2021).
Think of it this way: hydroquinone is a sprint, TXA is a steady jog — but one that won’t leave your skin winded and peeling.
For Melasma: Yes, It Works
Melasma is notoriously hard to treat — sun, hormones, heat, stress, and inflammation all make it worse. But multiple studies have shown that topical tranexamic acid for melasma can significantly lighten patches in 8–12 weeks when used consistently.
🧪 In a 2022 meta-analysis, TXA showed moderate to strong effectiveness for melasma in both topical and oral forms — and minimal side effects in most patients. That’s huge, considering how limited the options are for sensitive or darker skin tones that react poorly to hydroquinone.
Bonus: topical TXA can also boost the effects of other ingredients, like vitamin C and niacinamide, when used together.
For Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
TXA isn’t just for melasma — it’s also a solid pick for fading acne marks and PIH, especially in darker skin tones where post-breakout spots can last forever.
In one 2020 study, 3% TXA significantly reduced PIH within 8 weeks — and worked even better when combined with niacinamide. So if you’re dealing with leftover evidence of a breakout that’s long gone, TXA is your friend.
Safety, Side Effects & Who Should Avoid It
Is Tranexamic Acid Safe for Skin?
Short answer: yes. Longer answer: yes, but.
Topical TXA is generally well-tolerated — especially compared to the heavy hitters like hydroquinone or strong retinoids. That said, no skincare ingredient is drama-free.
Some people experience mild irritation, redness, or sensitivity — usually when starting a new product or layering too many actives. If your skin is already moody (looking at you, barrier damage babes), start slow and patch test.
Most formulations range from 2%–5%, and higher isn’t always better. Studies show that 2–3% TXA can be just as effective over time, especially when combined with other gentle brighteners like niacinamide or azelaic acid.
Who Should Be Cautious?
Pregnant or breastfeeding? Skip oral TXA — always talk to your doc first. But most derms say topical versions are fine (though research is limited).
Ultra-sensitive skin? Look for fragrance-free, minimalist formulas — no unnecessary botanicals, essential oils, or alcohol.
On blood thinners or clotting meds? Oral TXA might interact, but again, we’re talking about prescription-level usage. OTC skincare? You’re probably in the clear.
TXA is also a solid pick for darker skin tones, since it doesn’t carry the risk of hypopigmentation or rebound effects like hydroquinone sometimes does.
How to use tranexamic acid in your skincare routine
When Should You Use It — Morning or Night?
Here’s the good news: tranexamic acid plays well with others and fits into most routines without needing a total overhaul. You can use it once or twice a day, depending on the product and your skin’s vibe.
Morning use: Pair it with vitamin C, moisturizer, and SPF. This combo helps prevent UV-triggered pigmentation before it starts.
Night use: Layer with niacinamide or azelaic acid for a gentle brightening boost while your skin regenerates.
Choose one or the other if you’re sensitive — no need to double-dip unless your skin’s a seasoned pro.
What to Pair (and Not Pair) with TXA
TXA is the chill friend in your routine. She doesn’t pick fights, but she still has preferences.
✅ Pairs well with:
Vitamin C (AM brightening power couple)
Niacinamide (barrier-friendly + melanin-regulating)
SPF (non-negotiable for pigmentation)
Azelaic Acid (for acne-prone or redness-prone skin)
❌ Maybe skip if:
You’re already using strong actives like prescription retinoids or exfoliants and your barrier is irritated
The formula contains a ton of extra stuff — fragrances, essential oils, etc.
Pro tip: Apply TXA serum right after cleansing, then follow with moisturizer and sunscreen (AM) or heavier actives (PM). Always lock it in!
How Long Does It Take to Work?
This isn’t a “wake up flawless” kind of ingredient. Most users see results in 8–12 weeks, depending on severity and consistency. Melasma and post-acne marks can be stubborn, so patience is your best product.
⏳ Consistency = key. Skipping weeks = your hyperpigmentation wins.
Best Tranexamic Acid Products (Drugstore to Premium Picks)
There are a lot of TXA products out there — but not all of them are created equal. Some have the right percentage but horrible textures. Others bury TXA in a formula with a hundred other actives (👀 looking at you, glow cocktails). Here's what actually works.
Mid-End & Premium Picks
-
Murad Rapid Dark Spot Correcting Serum — TXA + niacinamide + glycolic acid. Luxurious feel, visible results in weeks.
👉 Check price on Amazon -
SkinMedica Even & Correct Advanced Brightening Treatment — Derm-backed, elegant formula. TXA + phenylethyl resorcinol for real results.
👉 Check price on Amazon -
Naturium Tranexamic Topical Acid 5% — Clean formula, great texture, gentle enough for sensitive skin.
👉 Check price on Amazon
Affordable & Effective
-
The INKEY List Tranexamic Acid Night Treatment — Affordable overnight formula. TXA + acai for gentle exfoliation.
👉 Check price on Amazon -
Good Molecules Discoloration Correcting Serum — TXA derivative (cetyl tranexamate), beginner-friendly, budget pick.
👉 Check price on Amazon
🧠 FAQs: Tranexamic Acid Edition
Can I use tranexamic acid while pregnant?
Short answer: Ask your OB-GYN.
Topical TXA hasn’t been shown to cause harm in pregnancy, but we don’t have a ton of long-term studies yet. If you're building a pregnancy-safe routine, many derms consider topical TXA lower-risk than oral forms — but still advise getting the green light from your doctor first. Think of it as probably fine but worth a check-in.
Does tranexamic acid bleach skin like hydroquinone?
Nope. TXA isn’t a bleach — it works by calming the overactive melanin signals, not by zapping pigment out altogether. That means it fades dark spots without lightening your natural skin tone. No ghosting here — just a smoother, more even glow.
What percentage of tranexamic acid should I start with?
Most studies use 2% to 5% in topical products.
You don’t need to max out to see results — even 2-3% TXA, especially when paired with other actives like niacinamide or vitamin C, can be super effective. If you’re sensitive, start low and slow. Your skin barrier will thank you.
Can I mix TXA with other actives?
Yes — and you should, for better results.
TXA plays well with vitamin C (brightening BFFs), niacinamide (team even tone), and sunscreen (non-negotiable). Just avoid layering it with heavy-duty acids or retinoids at the same time if you’re prone to irritation. Think: TXA AM / retinol PM = power couple.
How long does tranexamic acid take to work?
This isn’t a one-week wonder.
Most users start seeing improvement in 6–12 weeks with consistent use. Think of TXA like a slow-burn love story — subtle at first, but oh-so-worth it over time. Bonus: results tend to last longer than quick-fix ingredients.
Final Takeaway: What We Know About TXA (and What to Do With It)
Tranexamic acid might not be the flashiest name in your lineup — but when it comes to stubborn dark spots, it’s one of the most evidence-backed and sensitive-skin friendly options out there.
- ✅ It calms pigment production
- ✅ Works without bleaching
- ✅ Plays well with others (vitamin C, niacinamide, sunscreen)
- ✅ And doesn’t ghost your natural glow
Just give it time (6–12 weeks), pair it smartly, and you will start seeing that even, glowy skin peek through.
💫 Hero Product Recap
- Murad Rapid Dark Spot Correcting Serum – powerhouse with TXA + glycolic
- SkinMedica Even & Correct – luxe, effective, derm-approved
- Naturium Tranexamic Topical Acid 5% – clean, affordable, layers well
- The INKEY List Night Treatment – overnight boost on a budget
- Good Molecules Discoloration Serum – beginner-friendly + gentle
Want to dig deeper?
Expect steady, not instant— this evidence-based timeline shows when TXA results kick in.
Pairing TXA with strict UV protection accelerates gains, so here’s how sunscreen supports fading in studies.
If you want more than TXA in your toolkit, these proven ingredients layer well for faster fade.
References
Del Rosario E, Florell SR, Zone JJ, et al. Tranexamic acid for the treatment of melasma: A review and update. International Journal of Dermatology. 2022;61(2):147–155.
Lee HC, Thng TG, Goh CL. Oral tranexamic acid (TXA) in the treatment of melasma: A retrospective analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2016;75(2):385–392.
Kim HJ, Moon SH, Park KC. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100(1):adv00259.
Perper M, Eber AE, Fayne R, et al. Tranexamic acid in the treatment of melasma: A comprehensive review. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2020;21(3):371–377.
Maeda K, Naganuma M. Topical tranexamic acid improves melasma in Asian patients: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy. 2019;21(4):221–226.
Zhu YI, Kirsner RS. Tranexamic acid in dermatology: Beyond hemostasis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 2021;20(9):1006–1012.
Sardana K, Bansal P, Ghunawat S. Comparative efficacy of hydroquinone and tranexamic acid in melasma: A randomized trial. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2019;64(2):123–128.
Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, et al. Safety and efficacy of TXA in skin of color: A real-world review. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. 2023;16(1):36–42.