Do Collagen Supplements Really Work for Anti-Aging? (What Science Says)
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases—at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I truly believe in.
You’ve seen the hype: collagen powders, gummies, and even collagen coffee promising smoother skin, fewer wrinkles, and a youthful glow from the inside out. But is this just another beauty trend—or does science actually back it up?
Let’s break down what collagen is, how these supplements work, and what real research says about whether they’re worth your money.
🧬 What Is Collagen—and Why Do We Lose It?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It gives skin its firmness, structure, and elasticity—basically acting as scaffolding to keep everything lifted and smooth.
But starting in your mid-20s, you lose about 1% of collagen per year. Combine that with UV damage, poor diet, stress, and aging, and you’ve got the perfect recipe for thinner, drier, more wrinkled skin.
That’s where collagen supplements come in—at least in theory.
🧪 How Collagen Supplements Work (And Why They’re Not Just Protein Powder)
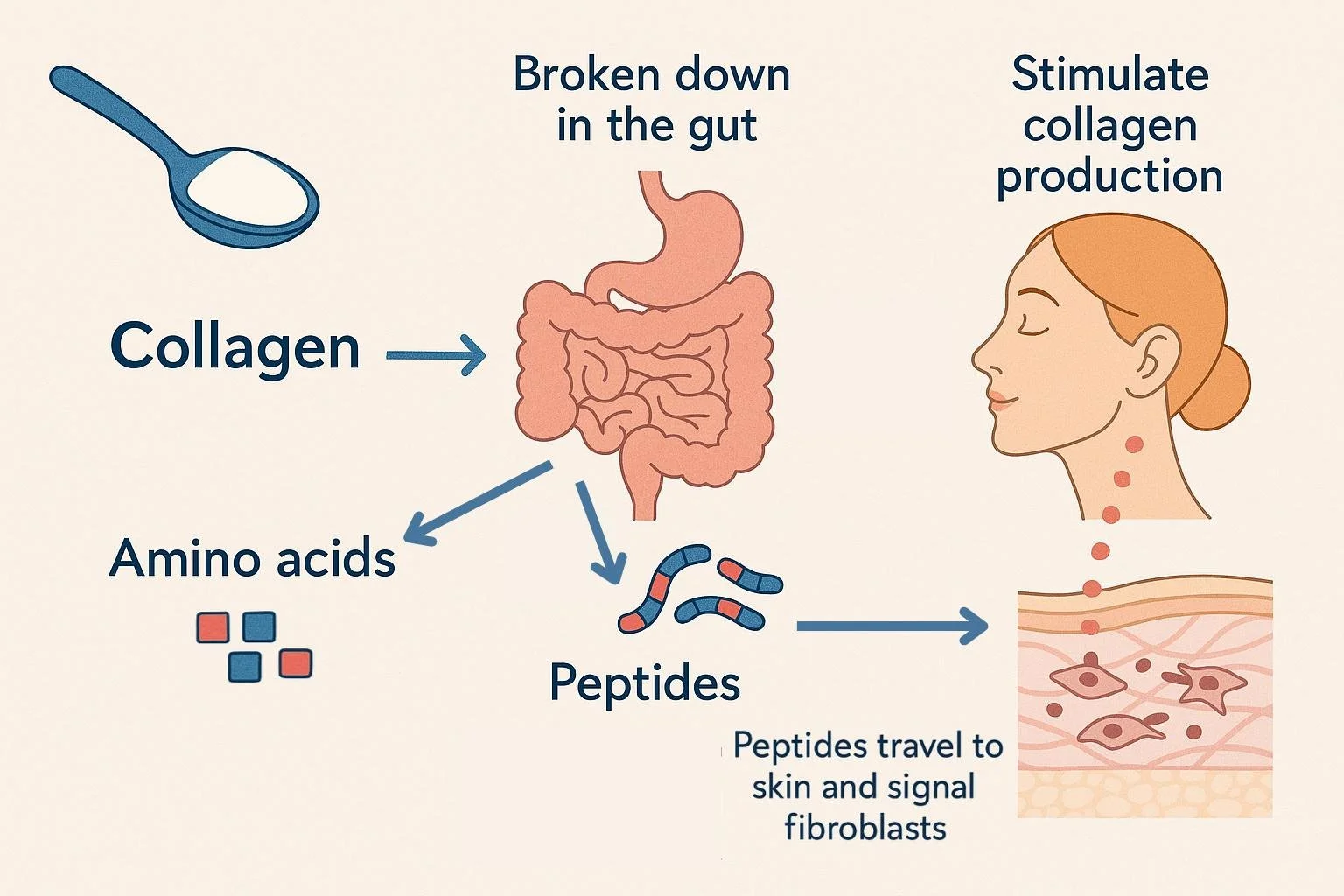
Most collagen supplements contain hydrolyzed collagen peptides—a fancy way of saying the collagen protein has been broken down into smaller pieces for better absorption.
Here's what happens when you take collagen:
It’s broken down in your gut into:
Amino acids (basic building blocks of protein)
Peptides (short chains of amino acids)
Some peptides are absorbed intact into your bloodstream
These peptides may travel to your skin and signal fibroblasts—the cells that produce collagen and elastin—to ramp up production
🧠 Why Peptides Matter (And What Regular Protein Can’t Do)
Yes, collagen provides amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline—but these alone aren’t the whole story.
Specific peptides, like Pro-Hyp, may act as messenger molecules, telling your body to produce more collagen
Regular protein doesn’t appear to trigger this same signaling effect
👉 That’s what makes collagen supplements more than “just protein.”
💡 Think of it like this:
Amino acids = the bricks
Peptides = the foreman telling your skin to build
🔬 Bonus: What’s Hydroxyproline?
Hydroxyproline isn’t one of the standard 20 amino acids. It’s formed when the body adds a hydroxyl group to proline—and that only happens during collagen production. It’s one reason collagen peptides are so unique, and why your body can’t get them in significant amounts from most foods.
📚 What the Science Says (In Plain English)
Over a dozen randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have found that taking 2.5–10g of hydrolyzed collagen peptides daily for 8–12 weeks can significantly improve:
✅ Skin hydration
✅ Elasticity
✅ Fine lines and wrinkle depth
Some studies used ultrasound or skin sensors; others relied on dermatologist grading or participant feedback. A few were funded by supplement companies, but independent reviews back up the same benefits.
🧠 Bottom line: Collagen supplements may not work overnight, but the science consistently supports their ability to improve skin appearance and structure with regular use.
🧬 Bonus: What Happens Under the Surface?
Human trials show results — but lab research helps explain why.
A 2010 molecular study in mice found that collagen peptides increased gene activity related to collagen type I, elastin, and hyaluronic acid synthase in skin tissue.
No self-reporting, no placebo bias—just a molecular signal that collagen peptides may actively stimulate collagen production at the cellular level.
🧭 Which Type of Collagen Should You Take?
Now that we know collagen supplements can work, the next question is:
Which type should you take? Marine, bovine, porcine—they all sound similar, but the source and collagen type can affect how your skin responds.
🧬 Marine vs. Bovine Collagen — and Why Type Matters
SourceTypesBenefitsNotesBovine (cow)Type I & IIISkin firmness + joint supportMost common, most studied, matches human collagen wellMarine (fish)Type ISkin, hair, nailsSmaller peptides, pescatarian-friendlyPorcine (pig)Type I & IIISimilar to bovineLess common in the U.S.
Type I is the most abundant collagen in your skin
Type III supports elasticity and structure alongside Type I
Bottom line: If you’re looking for collagen for skin and joints and don’t have dietary restrictions, bovine collagen is the most widely studied and reliable option.
If you avoid red meat or prefer pescatarian sources, marine collagen is a great alternative — and may absorb slightly more easily due to smaller peptides.
🟡 Note on Vegan Collagen:
There’s currently no true vegan collagen peptide supplement. Most plant-based options are collagen boosters — blends of nutrients (like vitamin C, zinc, biotin, and amino acids) that support collagen synthesis but don’t contain actual collagen. Lab-grown vegan collagen is in development, but not widely available yet.
🛒 Best Collagen Powders & Gummies
-
💪 Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Powder
💧 Unflavored, high-quality bovine collagen
🔢 10g per scoop – matches upper end of study range
👉 Check price on Amazon -
🍓 Garden of Life Collagen Beauty Gummies
💧 2.5g per serving + biotin, silica, and zinc
🔢 Matches minimum effective study dose
👉 Check price on Amazon -
🌊 Sports Research Marine Collagen Peptides
🐟 Hydrolyzed marine collagen from wild-caught fish
🔢 10g per scoop, pescatarian-friendly
👉 Check price on Amazon
❌ Common Mistakes
Expecting overnight results (8–12 weeks is the sweet spot)
Taking it sporadically (daily is best)
Forgetting vitamin C, which is needed to make collagen
Thinking all collagen is the same (type and source matter!)
🙋♀️ FAQ
Is collagen just glorified protein?
Not quite. Collagen peptides may signal your body to make more collagen—something general protein doesn’t do.
Can’t I just eat more protein instead?
Helpful, but most proteins don’t contain hydroxyproline or bioactive peptides like Pro-Hyp.
Is it safe during pregnancy?
Often yes, but always check with your doctor—especially if the supplement includes herbs or extras.
Marine vs. bovine—which should I choose?
Marine is great for skin and more bioavailable; bovine offers a broader set of collagen types. Choose based on your skin needs and dietary restrictions.
Is there a vegan collagen supplement?
No true vegan collagen peptides exist yet. Vegan “collagen” supplements are typically boosters — they support your body’s own collagen production but don’t contain collagen itself.
✨ Final Takeaway
Collagen supplements aren’t hype—they’re backed by solid science. When taken consistently at the right dose, they’ve been shown to improve hydration, firmness, and wrinkle depth in as little as 8–12 weeks.
Pair it with vitamin C, stay consistent, and give it time. Your skin may just thank you with a firmer, glowier version of itself.
Want to Dig Deeper?
Whatever you decide on supplements, daily UV protection remains the biggest lever, so make sure your sunscreen is dialed in.
To support collagen with topicals, combine antioxidants and retinoids, and this vitamin C guide shows evidence-backed picks.
If you want a short, vetted list to start with, these three derm-approved vitamin C serums keep it simple.
📚 References
Bolke, L., Schlippe, G., & Gerß, J., et al. (2019). A collagen supplement improves skin hydration, elasticity, roughness, and density: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, blind study. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 32(5), 219–223.
Choi, S. Y., Ko, E. J., & Lee, Y. H., et al. (2021). Effects of collagen tripeptide supplement on skin properties: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. International Journal of Dermatology, 60(10), 1316–1324.
de Miranda, R. C. G., Weimer, P., & Molinari, D. R., et al. (2021). Oral supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen improves skin elasticity, hydration, and dermal collagen density: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 13(11), 4201.
Ohara, H., Matsumoto, H., & Ito, K., et al. (2010). Comparison of quantity and structures of hydroxyproline-containing peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates from different sources. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (Tokyo), 56(3), 250–256.
Proksch, E., Segger, D., & Degwert, J., et al. (2023). Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 36(2), 67–74.